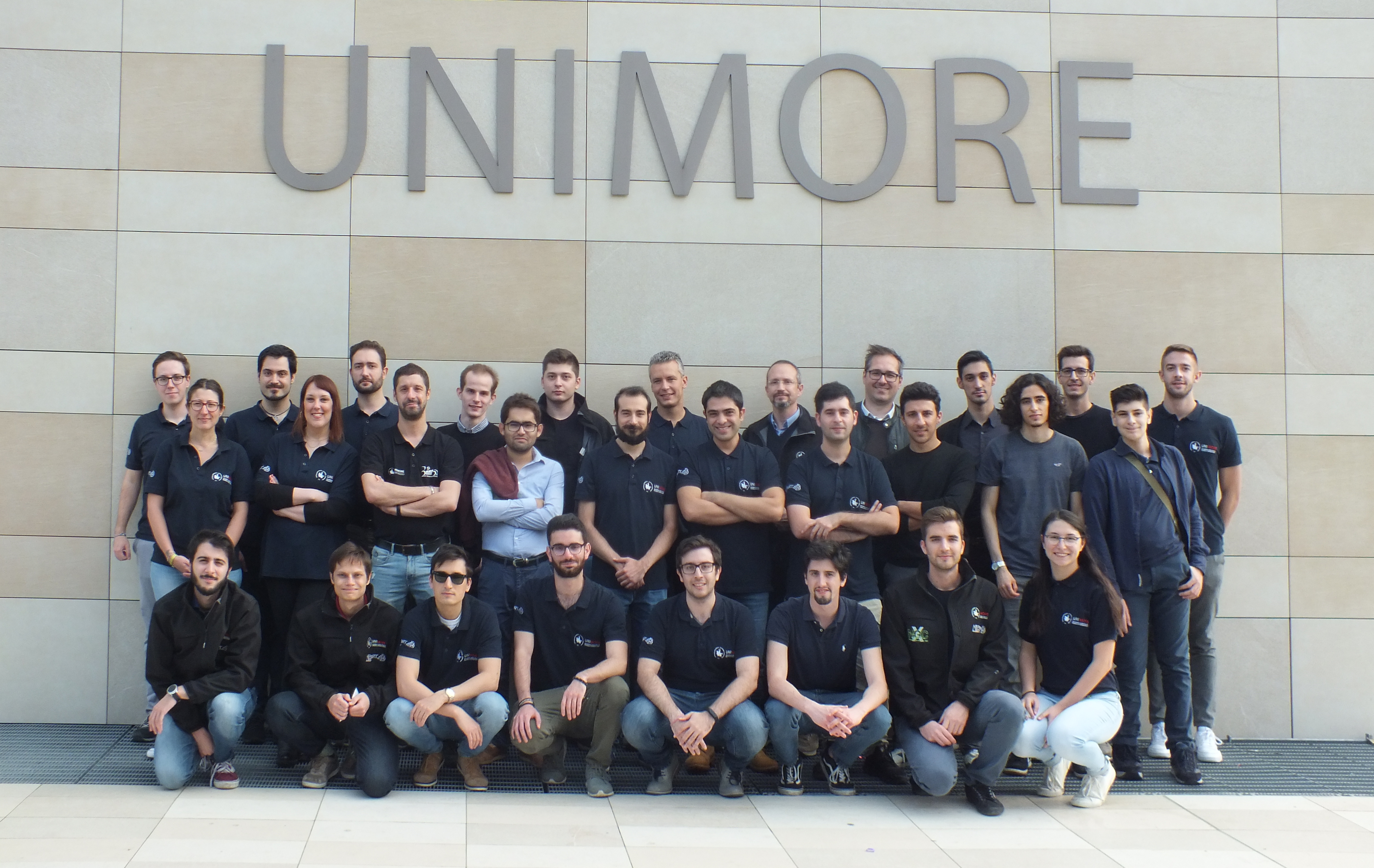
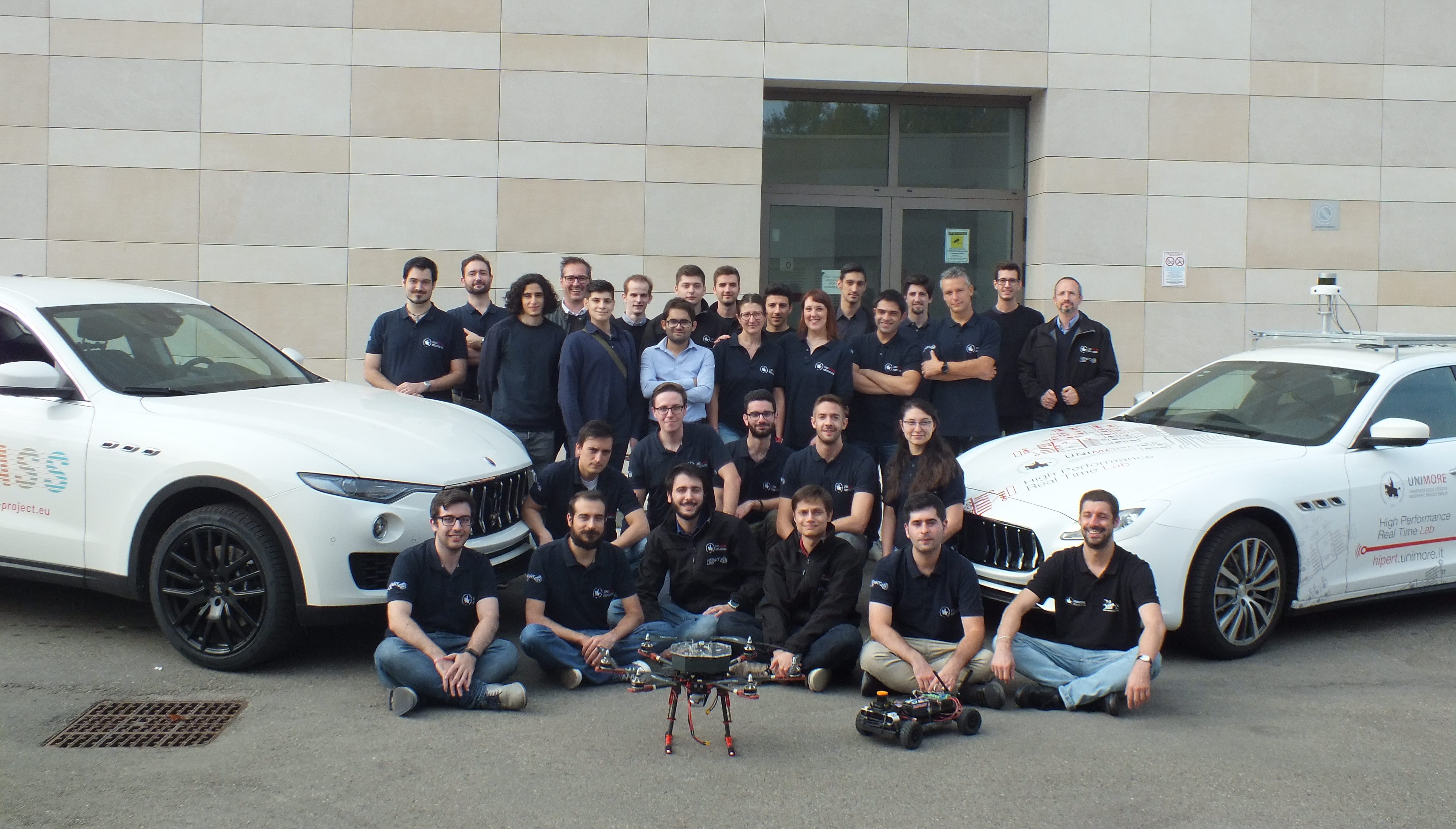



Who’s HiPeRT Lab?
The High-Performance Real-Time Laboratory (HiPeRT Lab) has been founded in 2012 at the University of Modena. It involves more than 40 researchers developing algorithmic and software solutions for high-performance real-time system. HiPeRT Lab’s mission is to predictably exploit the tremendous performance offered by next-generation embedded platforms in application domains where timing and safety requirements are crucial. To this end, the group acquired a strong expertise throughout the whole technological stack, from low-level hardware profiling and characterization, to Real-Time Operating Systems and Hypervisors, to predictable compilers and parallel programming models. The lab hosts multiple working prototypes, including autonomous vehicles (multiple cars, delivery bots, RC models, drones, etc.) and industrial automation systems. HiPeRT Lab is involved in several EU and industrial projects in automotive, avionics and industrial automation domains. It strongly believes in the technology transfer between academia and industry, fostering and promoting new collaborations for improving and devising the real-time systems of the future.
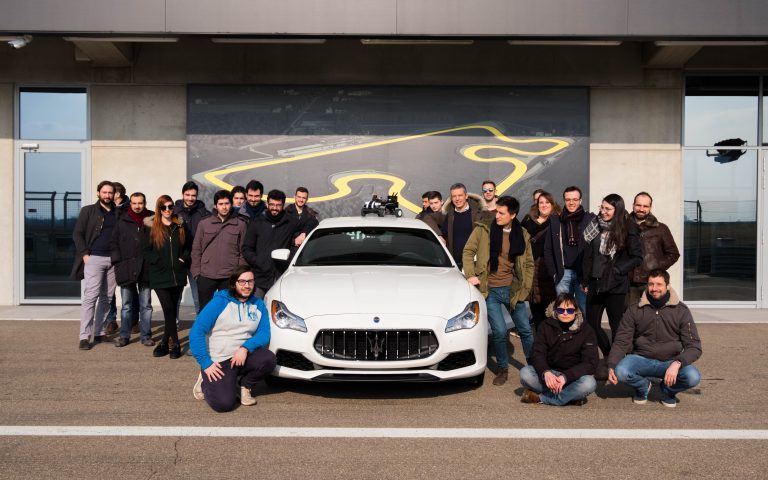
SELF-DRIVING CARS
AND AUTONOMOUS VEHICLES
The golden era of embedded super-computers entered a phase where hardware platforms are mature enough to power real production systems.
Especially, the dream of having self-driving autonomous vehicles is
quickly shaping, and both industries and academics are investing
resources in this direction. HiPeRT joins the effort with a framework of
technologies and software components aggregated in several L3/4
prototypes with full/semi-autonomous capabilities.
These efforts are supported both by industrial and public projects, and
cover multiple application domains: from “standard” to racing cars, from last-mile delivery
bots, to laser-guided vehicles for warehouse management, to autonomous
swarms of aerial and marine drones.
SELF-DRIVING CARS AND ATUONOMOUS VEHICLES
HiPeRT joins the effort with a framework of technologies and software components aggregated in several L3/4 prototypes with full/semi-autonomous capabilities. These efforts are supported both by industrial and public projects, and cover multiple application domains: from “standard” to racing cars, from last-mile delivery bots, to laser-guided vehicles for warehouse management, to autonomous swarms of aerial and marine drones.
REAL-TIME EMBEDDED SYSTEM
The mission of the Systems team in HiPeRT starts from hardware characterization and profiling and instruments hypervisors with novel software techniques that provide a real-time-enabling layer where multi-OS/RTOS solutions can be safely hosted guaranteeing the crucial Freedom-from-Interference property. Custom compiler optimisation and task profiling are keys to either control or know, respectively, the application's behaviour. This enables revolutionary memory-centric platform scheduling and predictable execution models on the one hand. On the other hand, rich, DAG-like task models are allocated on the architecture heterogeneity to minimise response time while avoiding any deviation.
HiPeRT Lab is in the core organization team of the F1/10 autonomous racing competition, which takes place twice per year and gathers a world-wide community of researchers, engineers and simply tech lovers for Autonomous Driving Systems. We also won the New York edition in 2019.
In the field of Artificial Intelligence, the HiPeRT Lab focuses on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) for object detection and segmentation, neural network quantization, meta-learning for automatic hyper-parameter tuning and mathematical optimization to strengthen the robustness of the methods.
REAL-TIME EMBEDDED SYSTEMS
The mission of the Systems team in HiPeRT starts from hardware characterization
and profiling and instruments hypervisors with novel software techniques that
provide a real-time-enabling layer where multi-OS/RTOS solutions can be safely
hosted guaranteeing the crucial Freedom-from-Interference property. Custom
compiler optimisation and task profiling are keys to either control or know,
respectively, the application’s behaviour. This enables revolutionary
memory-centric platform scheduling and predictable execution models on the one
hand. On the other hand, rich, DAG-like task models are allocated on the
architecture heterogeneity to minimise response time while avoiding any
deviation.
HIGH PERFORMANCE FOR EMBEDDED COMPUTING
HiPeRT Lab’s expertise in embedded computing involves programming models, compilers, architectures, benchmarking, performance engineering and state-of-the-art algorithm implementation in sensitive domains such as automotive, AI and industrial automation.
HiPeRT Lab’s tight collaboration with key industry players allows the lab to contribute in research and development of tailored solutions on cutting edge technologies such as NVIDIA integrated System-on-Chips and discrete GPUs, Xilinx FPGA platforms and Neural Network processors (e.g. Intel Movidius, Huawei NPU etc…)
RESEARCH PROJECTS

Shapefuture
ShapeFuture belongs to the Chips Act program. The project will drive innovation in fundamental Electronic Components and Systems (ECS) for integrated perception, cognition, AI-enabled decision making, and communications, for highly automated vehicles. The project will deliver advanced sensor fusion module with L4 decisional capabilities, running on automotive-level ECUs
Chips Act (Horizon), Grant Agreement: 101139996

Trace
TRACE will provide an integrated solution to support the synchromodal paradigm to improve logistics operation in terms of costs, emissions, time and fuel requirements.
UNIMORE/HiPeRT Lab is involved in the design of semi-autonomous platoons of cargo bikes, and their interaction with the Modena Automotive Smart Area cloud system.
Horizon, Grant Agreement: 101104278

dAIEDGE
The dAIEDGE Network of Excellence (NoE) aims to strengthen Europe’s AI ecosystem by supporting the development of advanced AI under the European Lighthouse for AI. It fosters collaboration among AI actors, helping the EU and the European Commission identify strategies for future developments. By promoting the exchange of ideas and cutting-edge concepts, it enhances innovation across sectors. The main objective is to advance Europe’s innovation and technology base, positioning the EU as a global leader in the data economy and AI applications.
Grant Agreement Number: 101120726

IMOCO4.E
IMOCO4.E targets to provide vertically distributed edge-to-cloud intelligence for machines, robots and other human-in-the-loop cyber-physical systems having actively controlled moving elements. They face ever-growing requirements on long-term energy efficiency, size, motion speed, precision, adaptability, self-diagnostic, secure connectivity or new human-cognitive features.
ECSEL (H2020), Grant Agreement: TBD 101007311

AI4CSM
AI4CSM strategic goals are analyzed through a set of strategic objectives to be achieved which address the realization of embedded intelligence for a secure connected, cooperative and autonomous mobility, for a climate neutral and Vision Zero transportation in 2050 through automotive intelligence sharing applications inside and outside the vehicles.
ECSEL (H2020), Grant Agreement: 101007326

FRACTAL
The objective of FRACTAL is to design a reliable computing node that will create a Cognitive Edge under industry standards, the building block of scalable Internet of Things , with the capability of learning how to improve its performance against the uncertainty of the environment.
ECSEL (H2020), Grant Agreement: 877056
NewControl
NewControl is an ECSEL JU project started in June 2019, and ended in March 2023. The focus was on reliable control of highly automated vehicles performing complex manoeuvres, such as overtaking at high speed. NewControl enabled fail-operational system that can accomplish those manoeuvres even in presence of failures and errors.
ECSEL (H2020), Grant Agreement: 826653-2

Prystine
Funded by the ECSEL JU program, the PRYSTINE started in May 2018, and ended in October 2021. PRYSTINE studies fail operational approaches related to autonomous driving, mostly focusing on ADAS-related applications. The project widened the solutions towards AI-enabled perception and control of highly automated vehicles.
ECSEL (H2020), Grant Agreement: 783190
Concluded projects
INDUSTRIAL COLLABORATION
Get In touch
Contacts
Address: Via Giuseppe Campi, 213/b, 41125 Modena MO
Phone: +39 059 205 5510
Email: hipert.info@unimore.it
Contacts
Address: Via Giuseppe Campi, 213/b, 41125 Modena MO
Phone: +39 059 205 5510
Email: hipert.info@unimore.it







































